One of the most common problems of the spine is the non -specific pain in the back of the back.According to the National Center for Health Statistics, 26-32% of the adult population suffers from chronic back pain.A common cause of this pain is osteochondrosis.
Osteocondrosis is premature and aging wear of intervertebral discs and vertebrae.Osteocondrosis can occur anywhere in the spine: cervical, chest, lumbar or lumbar.The lumbar segment is often influenced and lumbar osteochondrosis is developing.If you do not start treating in time, the disease can affect several departments simultaneously.
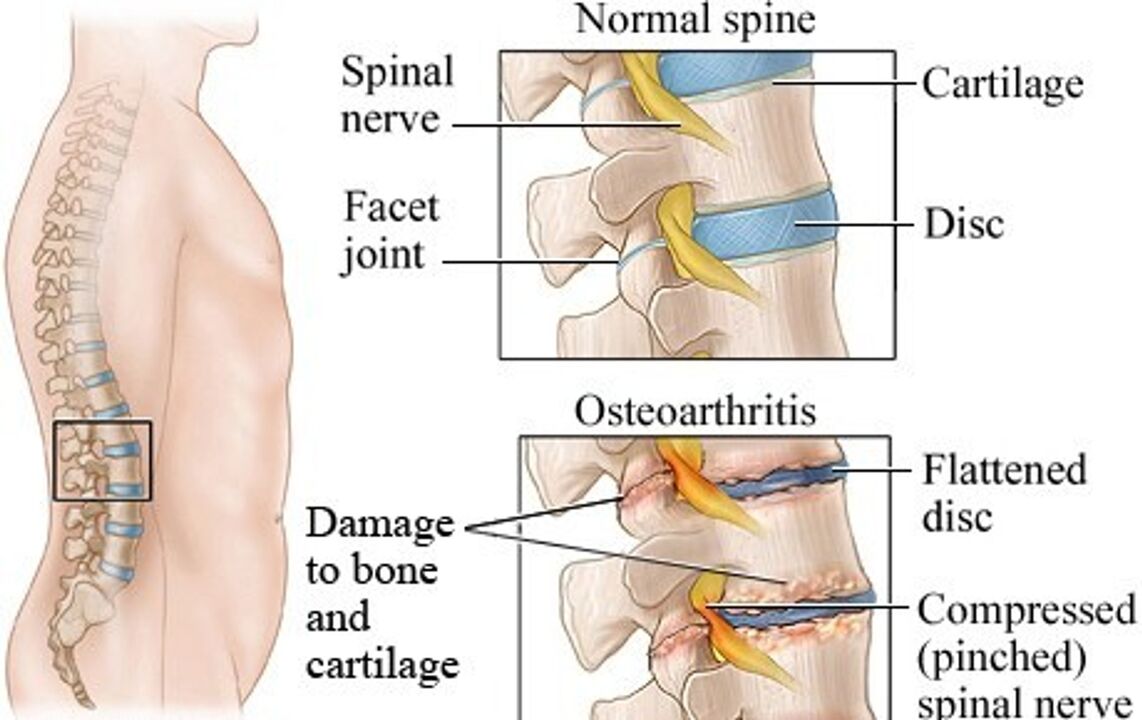
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar region is a chronic degenerative disease in which the tissue of the cartilage of the intervertebral discs in the lumbar region is destroyed.There are two main parts in the intervertebral disc: the nucleus and the fibrous ring.With an increase in the load, these structures are destroyed, which leads to the compression of the nerves and the appearance of acute pain.
Since the disease develops slowly, at the beginning its signs are difficult to notice.The patient does not pay attention or does not even understand exactly where it hurts.For this reason, they often come from the doctor at the time when intervertebral hernia develops.
The causes of osteochondosis
Lumbar osteocondrosis, like most diseases of the musculoskeletal system, has non -infectious etiology.Risk factors for the development of osteocondrosis are mainly associated with the motor activity of a person, lifestyle, professional working conditions and inheritance.Let's dwell on the main and perhaps the most important factors.
Violation of posture and reduction of motor activity.Given the modern rhythm of life, people must be in a position for a long time, whether it is an office job, to guide a car or study.For this reason, a large number of people have problems with the violation of posture, including scoliosis.When the posture is broken, the load on the spinal column is distributed in a non -uniform way: some discs are loaded more than others.The lumbar region suffers more than others.And in the case of the lumbar department, this load is many times more than on other departments.
Excessive physical activity.When a person does not play sports and back muscles are weak, intense training can damage.The exercises with an additional burden and an excessive load on the lumbar region lead to injuries, the intervertebral discs are worn in advance.
Excess of body weight and obesityIncreases the axial load on the spine.At the same time, the nutrition of intervertebral discs is disturbed due to which dystrophic processes develop.
Changes related to age.After 60 years, the fabric restoration processes slow down, therefore in the elderly the probability of developing higher intervertebral hernias.
Hereditary factors.If a person is naturally disturbed by the properties of cartilage and bone tissues, then his osteochondosis develops previously and the progress will be faster.
The first main signs and symptoms of lumbar osteochondosis
The intervertebral discs soften the shocks while walking, running and jumping.Due to the structural changes that accompany the lumbar osteochondrosis, this function suffers.
When intervertebral discs for osteochondrosis become thinner, this leads to an increase in the vulnerability of the nerves and blood vessels.The nerves are pinched and their diet is disturbed, acute pain and other symptoms of lumbar osteocondrosis appear.
Acuminated and chronic back pain- This is the main complaint with lumbar osteochondrosis.Personal activity, hypothermia, laying uncomfortable can cause pain.Sometimes the pain extends to the entire back and leg.
Tingling, burning and numbness (paresthesia) in the lower back and legs-The frequent symptom of lumbar osteochondrosis, which appears due to the compression of the nerves.
Increase in the tone of the back muscles in the lumbar regionIt can increase pain and lead to a decrease in mobility.
Phase of osteochondosis of the lumbar
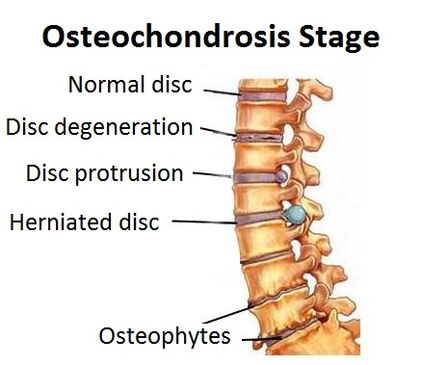
Changes in cartilage and bone tissue occur slowly.Depending on the prevalence of the pathological process, four stadiums of lumbar osteochdrosis are distinguished.
1st stadium.This is the beginning of the disease (Condro).The position of the gelatinous nucleus of the disc compared to the fiber fibers changes.This leads to the irritation of nerves and pain.Sometimes nothing hurts this phase.
Phase 2.Due to the shift of the discs, the intervertebral gap is reduced, the cracks appear in the discs.The nerves are compressed and the patient suffers from acute back pain.
Phase 3.The intervertebral discs are completely damaged, a fibrous ring is destroyed.At this stage, the risk of developing intervertebral hernia is high.Pain intensifies, appears more often and has a different character: from acute to chronic pain.
4th stadium.The disease applies to nearby tissues.In the lumbar region, mobility is reduced, pain also occurs with small changes in the position of the body.At this stage, intervertebral hernias and the risk of compression of the nerves and blood vessels in the lumbar region is developed.
Diagnosis of osteochondosis of the lumbar
If you are tormented by acute back pain both when you move and at rest, numbness of the legs - contact a neurologist.It will lead an inspection, will determine the probable cause of pain and prescribe the necessary diagnosis.
The main research methods are radiography and tomography.
- View, sighting and functional radiography of the spine in two projections.This method allows you to evaluate the conditions of the spine, but the soft tissues (for example, the muscles) and the cartilage in the images are not displayed.
- The computerized tomography allows you to obtain more information, since the images are obtained in different projections.Based on the results of the study, the doctor can determine the degree of damage to the lumbar column.
- Magnetic resonance imaging is the "gold standard" for the accurate diagnosis of "lumbar osteochondrosis".According to magnetic resonance imaging, the doctor can evaluate the conditions of the soft tissues and identify the hernia between the vertebrae.
Treatment of lumbar osteochondosis
After making a diagnosis, the neurologist individually selects the treatment.It depends on the stage of the disease and the severity of the symptoms.Most patients are helped by a complete conservative treatment (drug therapy, physiotherapy exercises, physiotherapy).If the patient is not better and serious complications develop, the operation is prescribed.
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment tasks:
- Stop pain.
- Reduce inflammation.
- Prevent the development of complications.
- Reduce the load on the spine by strengthening the muscles of the back.
- Reduce the compression of the nerves.
- In intervertebral hernia - Create conditions for its reabsorption and natural healing.
In the acute phase of the disease, the doctor mainly reduces pain and inflammation with analgesics and anti -inflammatory drugs.Subsequently, the neurologist elaborates a single program composed of physiotherapy, manual therapy and physiotherapy exercises.
PhysiotherapyIt is based on the use of physical factors: cold, heat, electric current, magnetic radiation, laser, etc.They help reduce pain intensity and improve tissue nutrition, which contributes to their natural restoration.
KinesitherapyIs active (exercise therapy) and passive (massage, traction).It allows you to strengthen the muscles of the back, relieve muscle tension, improve microcirculation and activate recovery processes.
Manual therapy and massageRemove an increase in muscle tone in the lower back, restore mobility.Because of this, the nutrition of the damaged area improves and the degree of pinching of the nerves decreases.
TapingOr Kinesiological taping is based on the use of elastic lacks, which are glued to the skin to weaken or improve muscle tone.So the muscle frame is strengthened, the microcirculation in the lumbar region improves and the distribution of the load on the spine is normalized.
Laser therapyIt is based on the use of low intensity laser radiation and its positive effects on the functioning of the cells.It contributes to the natural restoration of the intervertebral discs by improving their diet.
Plasma therapy(PRP therapy) -A method to improve regeneration processes.The injections of the patient's purified plasma stimulate his immunity.
Reflextotherapy, acupunctureImprove the flow of blood to the affected areas, reduce pain.
Shock waves therapy- This is the effect of high frequency waves on the affected area.It stimulates the natural processes of tissue regeneration and improves fabric nutrition.
Orthopedics- individual selection of corsets for further support of the spine.It partially allows the load on the spine.When wearing a corset, pain decreases, the mobility and quality of the patient's life increase.
Lumbar osteochondrosis is a chronic disease.It is important that the patient changes his lifestyle and learn to live with this disease.To do this, there are special educational programs that can improve the patient's quality of life.
The positive effect of the conservative treatment is obtained in 2-3 months.If this treatment is ineffective, the operation is prescribed.
Operation
With the development of intervertebral hernias of the lumbar department, minimally invasive surgical operations are performed.The choice in the direction of the neurosurgical treatment is made with special indications, in serious, threatening the patient's life.
The operation is a complex invasive treatment method associated with risks.During or after surgery, complications can develop.And the success of the treatment also depends on postoperative rehabilitation, which includes conservative therapy methods and orthopedic correction.
Do not postpone the treatment
Lumbar osteochondrosis is a progressive disease.If it is not detected over time and does not start treating it, it can lead to disability and decrease in the quality of life.Over time, several parts of the spine are affected, the pain made of acute goes into a chronic.
The timely prevention of symptoms and the treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis in the initial stages can prevent the development of the disease and a deterioration of the condition.